Minimizing domain bias when adapting sentiment analysis techniques to the legal domain 
Advised by: Amal Shehan Perera, Nisansa de Silva
University of Moratuwa
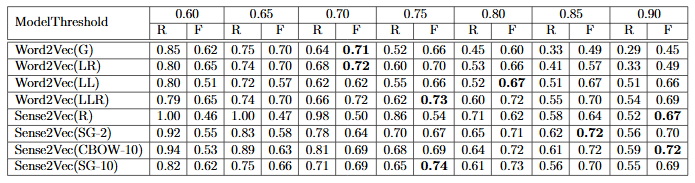
Sentiment Analysis can be considered as an integral part of Natural Language Processing with a wide variety of significant use cases related to different application domains. Analyzing sentiments of descriptions that are given in Legal Opinion Texts has the potential to be applied in several legal information extraction tasks such as predicting the judgement of a legal case, predicting the winning party of a legal case, and identifying contradictory opinions and statements. However, the lack of annotated datasets for legal sentiment analysis imposes a major challenge when developing automatic approaches for legal sentiment analysis using supervised learning. In this work, we demonstrate an effective approach to develop reliable sentiment annotators for legal domain while utilizing a minimum number of resources. In that regard, we made use of domain adaptation techniques based on transfer learning, where a dataset from a high resource source domain is adapted to the target domain (legal opinion text domain). In this work, we have come up with a novel approach based on domain specific word representations to minimize the drawbacks that can be caused due to the differences in language semantics between the source and target domains when adapting a dataset from a source domain to a target domain. This novel approach is based on the observations that were derived using several word representational and language modelling techniques that were trained using legal domain specific copora. In order to evaluate different word representational techniques in the legal domain, we have prepared a legal domain specific context based verb similarity dataset named LeCoVe . The experiments carried out within this research work demonstrate that our approach to develop sentiment annotators for legal domain in a low resource setting is successful with promising results and significant improvements over existing works
Keywords: Natural Language Processing | Machine Learning / Deep Learning | Law | Sentiment Analysis | Word Representation | Semantic Analysis |
